Consulting services can provide valuable insights, strategic guidance, pecialized
1200 West Walnut Hills Ln, Suite # 2550, Irving, Texas 75038.
Welcome to our First Cloud Inc
Project management services specialize in planning, coordinating, and executing projects based on specific requirements and constraints. They oversee various project activities, from inception to completion, with a focus on establishing and maintaining project milestones and schedules. The primary objective is to ensure the project’s timely and budget-conscious completion.
These services aid organizations in achieving project goals and objectives within defined scope, timeframes, and financial parameters. They facilitate resource optimization and integration to drive the attainment of project objectives effectively. Central to this process is the development of a comprehensive project plan, which outlines overarching goals, specific objectives, tasks, strategies for goal achievement, and resource requirements.

Project managers play a crucial role in establishing both the overall project budget and specific timelines for task completion. As they oversee the project plan, project management services adhere to recognized frameworks to guarantee precise and unbiased reporting. In the event of a missed milestone, project planners and managers must promptly implement corrective measures.
Some criteria to consider when selecting project management services include:
Project management begins with planning to achieve a goal. Many questions about a project must be considered before the project even begins:
Documentation used throughout a project’s management is known as the project plan and includes:
Effective communication is a vital component of project management that must be maintained consistently throughout the project’s duration. It’s imperative that all stakeholders receive regular updates through various channels such as email, meetings, conference calls, or by accessing a project dashboard. By ensuring open communication during every phase of the project, potential costly rework can be avoided down the line.
Organizing and monitoring a project can be facilitated through dedicated tools. These tools range from simple methods like tracking progress on a whiteboard to more sophisticated options such as specialized project management software. Project managers have the flexibility to create charts using word processing or spreadsheet programs, or they can utilize specialized software designed for project management. Examples of project management tools include:
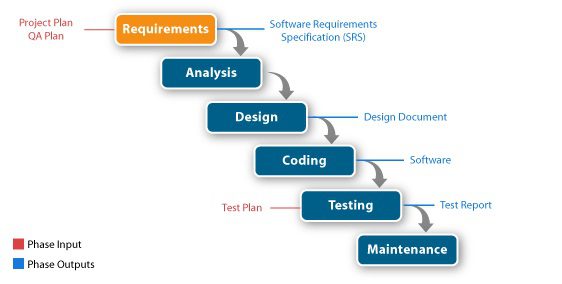
The traditional approach to project management is based on sequential steps. It has evolved to handle projects that clearly state a need, target date, and cost. The steps may vary by individual organization and usually include:
The waterfall model is often used in the software development process. The steps flow sequentially from one to the next like levels of a waterfall.
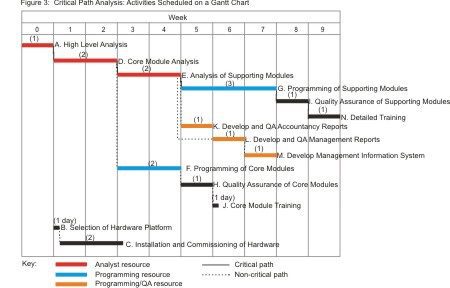
Critical chain project management (CCPM) allows for physical and human resource limitations by designing the project to deal with uncertainties. A critical path of steps is identified to give priority to the longest sequence of tasks with resource constraints. The constrained resources are known as the critical chain.
The project plan may undergo resource leveling, the process of resolving conflicts of a person’s or machine’s time. Because some tasks may be delayed due to conflict, other tasks must be shortened so that the project can still be completed by the target date. In some cases it is advisable to contract out sub-projects to eliminate resource conflict.
Based on the frequent change and uncertainty, extreme project management is designed for projects with high stakes and short deadlines. Extreme projects place emphasis on innovation and quality of life. Requirements can change rapidly. The focus of extreme project management is less on templates and more on leadership, because a leader can help navigate a rapidly changing environment.
One of the newest methods of project management is agile project management, often used in software development. Emphasis is placed on an integrated team of developers, managers, quality assurance, and customers and open communication is a key to the effectiveness of this method. Short-term deliverables called sprints allow for testing and changes.
A strategic form of project management that is driven by the vision, mission, and values of a business, project-based management has six stages:
Event-chain methodology recognizes that certain risks are taken in project management that could delay or speed up outcomes. Scenarios for time-related processes can be determined by modeling these uncertainties. Project managers can use this method to determine if a chain of events could be triggered by a specific task and plan to avoid or achieve that process.
The Projects in Controlled Environments (PRINCE2) methodology is used extensively in the United Kingdom government. It is a flexible method designed to balance current business operations and a need to transform those operations in order to remain competitive. The process itself is structured around managing the six project variables of costs, timescales, quality, scope, risk, and benefits.
Projects Integrating Sustainable Methods (PRiSM) is used to align project delivery and sustainability. Although similar to PRINCE2, it differs because long-term organizational impacts are considered with this methodology.
The lean methodology is based on the principle of lean manufacturing or lean enterprise that value for the customer is of utmost importance. Any steps that do not create value for the customer are considered wasteful and should be eliminated. Lean is based on four steps to be performed in a cycle of continuous improvement:
The Benefits realized methodology is based on looking at potential outcomes and defining the measure of their potential benefits. A quantitative basis is used to make decisions in this methodology. Plans are reviewed and implemented keeping the investment in mind.
Methodology | Structured | Timeline | Project Type |
Traditional (Waterfall) | Highly | Any | Any |
Critical Chain | Moderately | Any | Any |
Extreme | Less | Short | Software |
Agile | Less | Short | Software |
Process-Based | Highly | Any | Any |
Event-Chain | Moderately | Any | Any |
PRINCE2 | Less | Any | Any |
PRISM | Moderately | Long | Any |
Lean | Moderately | Any | Any |
Benefits Realized | Highly | Any | Any |
A project manager is responsible for planning and executing a project. He or she leads the team in all aspects of management and is responsible for delegating tasks. A project manager may be employed by the company requiring the work or may be brought in from the outside. A project manager has full responsibility for the project in addition to the authority to complete it.
Some responsibilities of the project manager include:
A skilled project manager can manage any project regardless of industry-specific knowledge. Many colleges offer programs for certification in project management. Organizations such as Project Management Institute (PMI) offer several types of certification based on level of experience or preferred methodology.
A project manager may be certified or expert in: